Your Daily eNewsletter
Content by SHW Research Team
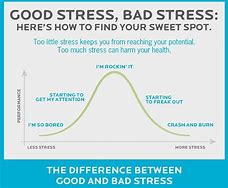
Hormonal Response: Stress induces a hormonal reaction in the body, chiefly the secretion of adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones ready the body to confront perceived threats.
Physical Symptoms: Stress can physically manifest, leading to headaches, muscle tension, chest pain, and fatigue, as well as digestive problems like upset stomach and diarrhea.
Mental and Emotional Impact: Prolonged stress can impair mental health, causing anxiety, depression, and irritability, along with cognitive difficulties such as forgetfulness and concentration issues.
Gender Differences: Typically, women are more susceptible to the physical symptoms of stress than men. Conversely, men are likelier to seek escape from stress and might show fewer physical symptoms.
Global Prevalence: Stress is a widespread concern globally. A 2021 Gallup poll revealed that 41% of adults around the world reported feeling a great deal of stress.
Workplace Stress: In the U.S., job-related stress is a major issue, with numerous adults identifying financial and work concerns as primary stressors.
Health Risks: Persistent stress can heighten the risk of serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and mental health conditions.
Stress Management: Regular exercise, mindfulness, sufficient sleep, and social support are effective stress management strategies.
Knowing these facts can aid in better stress recognition and management.




Leave a comment