
Content by Julie Fields-Certified Nutritionists
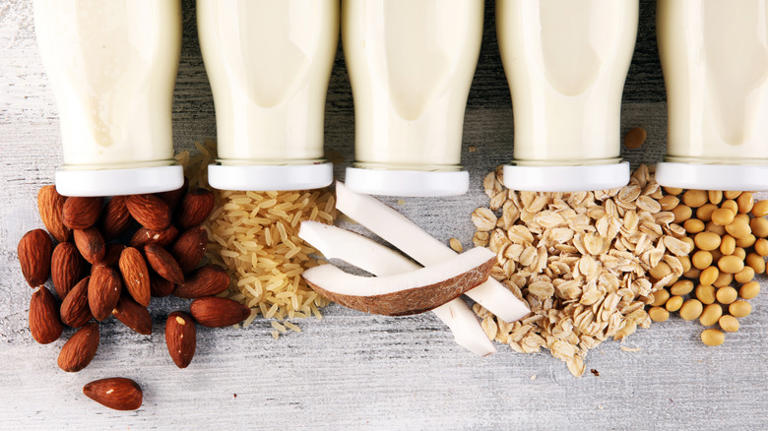
Milk is a nutritious beverage that provides protein, calcium, vitamin D and other essential nutrients. However, some people may prefer or need to avoid dairy milk for various reasons, such as allergies, lactose intolerance, veganism or personal preference. Fortunately, there are many plant-based milk alternatives available, such as soy, almond, oat, coconut and pea milk. But how do they compare to dairy milk in terms of sugar content and quality?
Sugar is a type of carbohydrate that provides energy for the body. However, not all sugars are the same. There are natural sugars, such as lactose in dairy milk and maltose in oat milk, and added sugars, such as sucrose, high-fructose corn syrup, honey and maple syrup. Added sugars are often used to enhance the flavor, texture and shelf life of processed foods and beverages, but they can also contribute to excess calories, weight gain, tooth decay and chronic diseases, such as diabetes and heart disease. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting added sugars to less than 10% of total daily calories, which is about 50 grams or 12 teaspoons for a 2,000-calorie diet.
According to the Nutrition Facts label, one cup of low-fat dairy milk contains 100 calories, 8 grams of protein, 30% of the daily value (DV) of calcium, 25% of the DV of vitamin D and 13 grams of sugar, all of which are natural sugars from lactose. Unsweetened plant-based milk alternatives vary in their nutrition content, depending on the plant source, processing method and fortification. Here is a brief comparison of some common plant-based milk alternatives and their sugar content per cup:
- Soy milk: 80 calories, 7 grams of protein, 30% of the DV of calcium, 15% of the DV of vitamin D and 1 gram of sugar, which is natural sugar from soybeans.
- Almond milk: 30 calories, 1 gram of protein, 45% of the DV of calcium, 25% of the DV of vitamin D and 0 grams of sugar, which means no natural or added sugars.
- Oat milk: 120 calories, 4 grams of protein, 35% of the DV of calcium, 20% of the DV of vitamin D and 7 grams of sugar, most of which are natural sugars from maltose.
- Coconut milk: 45 calories, 0 grams of protein, 45% of the DV of calcium, 25% of the DV of vitamin D and 0 grams of sugar, which means no natural or added sugars.
- Pea milk: 70 calories, 8 grams of protein, 45% of the DV of calcium, 30% of the DV of vitamin D and 0 grams of sugar, which means no natural or added sugars.
As you can see, plant-based milk alternatives have different amounts and types of sugar than dairy milk. Some of them have no sugar at all, while others have natural sugars from the plant source. However, some plant-based milk alternatives may also contain added sugars, especially if they are sweetened or flavored. For example, one cup of vanilla almond milk may have 16 grams of added sugar, which is more than the amount of natural sugar in dairy milk. Therefore, it is important to check the ingredients list and the Nutrition Facts label for the amount and source of sugar in the product. The healthiest options have no added sugars, so try to choose unsweetened versions. Plant milk tends to be naturally sweet anyway.
In conclusion, dairy milk and plant-based milk alternatives are not nutritionally equal, and sugar is one of the factors that differentiate them. While dairy milk has natural sugar from lactose, plant-based milk alternatives may have natural sugar from the plant source, added sugar or no sugar at all. The best choice depends on your individual needs, preferences and goals. However, as a general rule, limit your intake of added sugars and opt for unsweetened versions of plant-based milk alternatives whenever possible.



Leave a comment